-
Engineering and Architecture
Exams
Colleges
Predictors
Resources
-
Computer Application and IT
Quick Links
Colleges
-
Pharmacy
Colleges
Resources
-
Hospitality and Tourism
Colleges
Resources
Diploma Colleges
-
Competition
Other Exams
Resources
-
School
Exams
Top Schools
Products & Resources
-
Study Abroad
Top Countries
Resources
-
Arts, Commerce & Sciences
Exams
Colleges
Upcoming Events
Resources
-
Management and Business Administration
Colleges & Courses
Predictors
-
Learn
Law Preparation
MBA Preparation
Engineering Preparation
Medical Preparation
-
Online Courses and Certifications
Top Streams
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
Resources
-
Medicine and Allied Sciences
Colleges
Predictors
Resources
-
Law
Resources
Colleges
-
Animation and Design
Exams
Predictors & Articles
Colleges
Resources
-
Media, Mass Communication and Journalism
Colleges
Resources
-
Finance & Accounts
Top Courses & Careers
Colleges
Get Answers to all your Questions


Using the mean value theorem, prove that there is a point on the curve 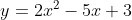 between the points A(1,0) and B(2, 1), where the tangent is parallel to the chord AB. Also, find that point.
between the points A(1,0) and B(2, 1), where the tangent is parallel to the chord AB. Also, find that point.
Answers (1)
Solution
Given: in [1,2]
Now, we have to show that f(x) verify the Mean Value Theorem
First of all, Conditions of Mean Value theorem are:
a) f(x) is continuous at (a,b)
b) f(x) is derivable at (a,b)
If both the conditions are satisfied, then there exist some ‘c’ in (a,b) such that
Condition 1:
since, f(x) is a polynomial and we know that, every polynomial function is continuous for all
is continuous at
Hence, condition 1 is satisfied.
Condition 2
since, f(x) is a polynomial and every polynomial function is differentiable for all
is differentiable at [1, 2]
Hence, condition 2 is satisfied.
Thus, Mean Value Theorem is applicable to the given function.
Now,
Then, there exist such that
Put x=c in equation, we get
By Mean Value Theorem,
So, value of
Thus, Mean Value Theorem is verified.
Put in given equation
, we have
Similar Questions
- 100 g of liquid A (molar mass 140 g mol^-1) was dissolved in 1000 g of liquid B (molar mass 180 g mol^-1).The vapour pressure of pure liquid B was found to be 500 torr.
- 100 turn rectangular coil ABCD (in X-Y plane) is hung from one arm of a balance (shown in figure). A mass 500 g is added to the other arm to balance the weight of the coil.
- 100m long antenna is mounted on a 500m tall building The complex can become a transmission tower for waves with λ (a) ~ 400 m (b) ~ 25 m (c) ~ 150 m (d) ~ 2400 m

