Browse by Stream
-
Engineering and Architecture
Exams
Colleges
Predictors
Resources
-
Computer Application and IT
Quick Links
Colleges
-
Pharmacy
Colleges
Resources
-
Hospitality and Tourism
Colleges
Resources
Diploma Colleges
-
Competition
Other Exams
Resources
-
School
Exams
Top Schools
Products & Resources
-
Study Abroad
Top Countries
Resources
-
Arts, Commerce & Sciences
Exams
Colleges
Upcoming Events
Resources
-
Management and Business Administration
Colleges & Courses
Predictors
-
Learn
Law Preparation
MBA Preparation
Engineering Preparation
Medical Preparation
-
Online Courses and Certifications
Top Streams
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
Resources
-
Medicine and Allied Sciences
Colleges
Predictors
Resources
-
Law
Resources
Colleges
-
Animation and Design
Exams
Predictors & Articles
Colleges
Resources
-
Media, Mass Communication and Journalism
Colleges
Resources
-
Finance & Accounts
Top Courses & Careers
Colleges
Get Answers to all your Questions


- Home
- Engineering
- The largest and the shortest distance of the earth from are r1 and r2. It’s distance from the sun when it is perpendicular to the major-axis
The largest and the shortest distance of the earth from are r1 and r2. It’s the distance from the sun when it is perpendicular to the major axis of the orbit drawn from the sun.
Option 1)
Option 2)
Option 3)
Option 4)
Answers (1)
As we learnt in
Velocity of planet in terms of Eccentricity -
Velocity of the planet at apogee
- wherein
Eccentricity (e) =
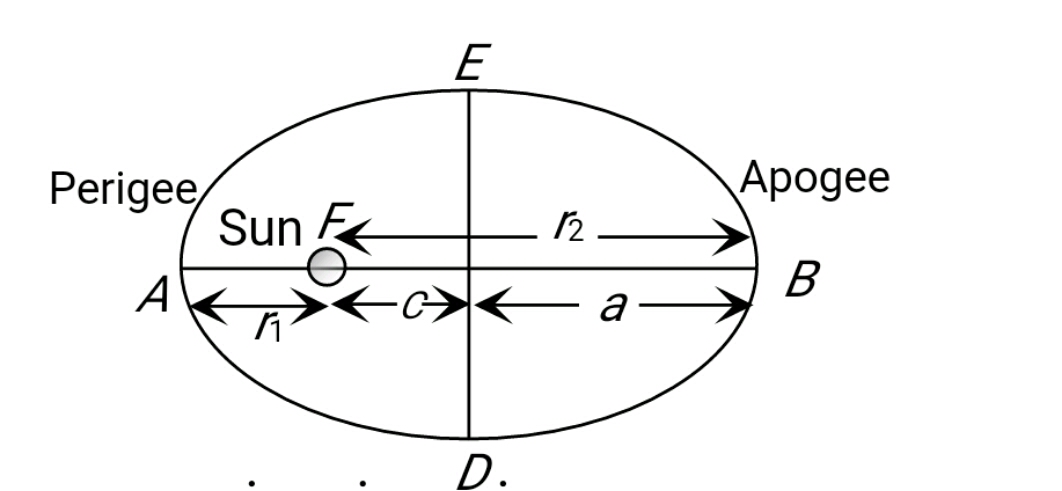
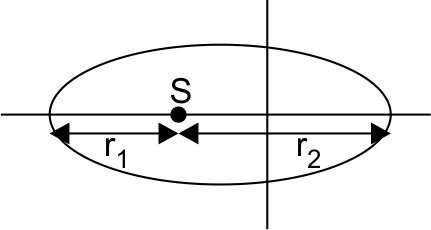
The position of a particle moving in an elliptical orbit is represented as
is perpendicular distance of particle from focus and e is eccentricity of ellipse
View full answer

