-
Engineering and Architecture
Exams
Colleges
Predictors
Resources
-
Computer Application and IT
Quick Links
Colleges
-
Pharmacy
Colleges
Resources
-
Hospitality and Tourism
Colleges
Resources
Diploma Colleges
-
Competition
Other Exams
Resources
-
School
Exams
Top Schools
Products & Resources
-
Study Abroad
Top Countries
Resources
-
Arts, Commerce & Sciences
Colleges
Upcoming Events
Resources
-
Management and Business Administration
Exams
Colleges & Courses
Predictors
-
Learn
Law Preparation
MBA Preparation
Engineering Preparation
Medical Preparation
-
Online Courses and Certifications
Top Streams
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
Resources
-
Medicine and Allied Sciences
Colleges
Predictors
Resources
-
Law
Resources
Colleges
-
Animation and Design
Exams
Predictors & Articles
Colleges
Resources
-
Media, Mass Communication and Journalism
Colleges
Resources
-
Finance & Accounts
Top Courses & Careers
Colleges
Get Answers to all your Questions


All Questions
The graph which depicts the results of Rutherford gold foil experiment with particles is:
: Scattering angle Y : Number of scattered
particles detected (Plots are schematic and not to scale)
Option: 1 
Option: 2 
Option: 3 
Option: 4 
As
Here when Sin will be zero then Y will tend to infinity.
and that is satisfied by the only option 1
So the correct option is 1.
View Full Answer(1)The time period of revolution of electron in its ground state orbit in a hydrogen atom is . The frequency of revolution of the electron in its first excited state (in s-1) is:-
Option: 1
Option: 2
Option: 3
Option: 4
The velocity of the nth orbit
the radius of the nth orbit
and
So, option (3) is correct.
View Full Answer(1)Crack CUET with india's "Best Teachers"
- HD Video Lectures
- Unlimited Mock Tests
- Faculty Support

The energy required to ionised a hydrogen like ion in its ground state is 9 Rydbergs. What is the wavelength (in nm) of the radiation emitted when the electron in this ion jumps from the second excited state to the ground state ?
Option: 1 11.4
Option: 2 24.2
Option: 3 8.6
Option: 4 35.8
Wavelength
Hence the correct option is (1).
View Full Answer(1)The first member of the Balmer series of the hydrogen atom has a wavelength of 6561 . The wavelength of the second member of the Balmer series (in nm ) is _______ .
Option: 1 486
Option: 2 972
Option: 3 986
Option: 4 586
JEE Main high-scoring chapters and topics
Study 40% syllabus and score up to 100% marks in JEE
The activity of a radioactive sample falls from to
in 30 minutes. Its half life ( in minutes ) is close to :
Option: 1 62
Option: 2 72
Option: 3 66
Option: 4 52
Activity at any time is given as
After half-life,
so
Now for
from( (i) and (ii)
Hence the correct option is (1).
View Full Answer(1)A radioactive sample has an average life of 30 ms and is decaying. A capacitor of capacitance 200 is first charged and later connected with resistor
If the ratio of charge on capacitor to the activity of radioactive sample is fixed with respect to time then the value of 'R' should be ______
.

Let be the initial change on the capacitor
Discharging of capacitor condition.
Activity after time t
NEET 2024 Most scoring concepts
- Just Study 32% of the NEET syllabus and Score up to 100% marks
An electron and proton are separated by a large distance. The electron starts approaching the proton with energy The proton captures the electrons and forms a hydrogen atom in second excited state. The resulting photon is incident on a photosensitive metal of threshold wavelength
. What is the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectron?
Option: 1
Option: 2
Option: 3
Option: 4
Energy lost by electron=Energy of emitted photon
By Einstein's photoelectric equation
The correct option is (2)
Consider the following statements : A. Atoms of each element emit characteristics spectrum. B. According to Bohr's Postulate, an electron in a hydrogen atom, revolves in a certain stationary orbit. C. The density of nuclear matter depends on the size of the nucleus. D. A free neutron is stable but a free proton decay is possible. E. Radioactivity is an indication of the instability of nuclei. Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Option: 1 A, B, C, D and E
Option: 2 A, B and E only
Option: 3 B and D only
Option: 4 A, C and E only
A free neutron is unstable
Density of nuclear matter is constant for all elements.
The correct option is (2)
Crack CUET with india's "Best Teachers"
- HD Video Lectures
- Unlimited Mock Tests
- Faculty Support

The of molybdenum has wavelength
. If the energy of a molybdenum atoms with a
electron knocked out is
, the energy of this atom when an L electron is knocked out will be ________
(Round off to the nearest integer)
- Energy when an L shell-electron is knocked out
- Energy when a K shell-electron is knocked out
wavelength emitted during knocking out of L-electron
A particular hydrogen-like ion emits radiation of frequency 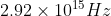 when it makes the transition from n = 3 to n = 1, The frequency in Hz of radiation emitted in transition from n =2 to n= 1 will be :
when it makes the transition from n = 3 to n = 1, The frequency in Hz of radiation emitted in transition from n =2 to n= 1 will be :
Option: 1 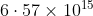
Option: 2 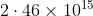
Option: 3 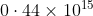
Option: 4 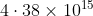
The correct option is (2)
JEE Main high-scoring chapters and topics
Study 40% syllabus and score up to 100% marks in JEE


