-
Engineering and Architecture
Exams
Colleges
Predictors
Resources
-
Computer Application and IT
Quick Links
Colleges
-
Pharmacy
Colleges
Resources
-
Hospitality and Tourism
Colleges
Resources
Diploma Colleges
-
Competition
Other Exams
Resources
-
School
Exams
Top Schools
Products & Resources
-
Study Abroad
Top Countries
Resources
-
Arts, Commerce & Sciences
Exams
Colleges
Upcoming Events
Resources
-
Management and Business Administration
Colleges & Courses
Predictors
-
Learn
Law Preparation
MBA Preparation
Engineering Preparation
Medical Preparation
-
Online Courses and Certifications
Top Streams
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
Resources
-
Medicine and Allied Sciences
Colleges
Predictors
Resources
-
Law
Resources
Colleges
-
Animation and Design
Exams
Predictors & Articles
Colleges
Resources
-
Media, Mass Communication and Journalism
Colleges
Resources
-
Finance & Accounts
Top Courses & Careers
Colleges
Get Answers to all your Questions


All Questions
The most abundant elements by mass in the body of a healthy human adult are : Oxygen (61.4%); Carbon (22.9%), Hydrogen (10.0%); and Nitrogen (2.6%). The weight (in kg) which a 75 kg person would gain if all atoms are replaced by
atoms is :
Option: 1 7.5
Option: 2 10
Option: 3 15
Option: 4 37.5
Given that
Mass of the person = 75 kg
Mass of 1H1 present in person = 10% of 75 kg = 7.5 kg
Since Mass of 1H2 is double the Mass of 1H1
So, Mass of 1H2 will be in person = 2 X 7.5 kg =15 kg
Thus, increase in weight = 15 - 7.5 = 7.5 kg
Therefore, Option (1) is correct
View Full Answer(1)- #Classification of elements and periodicity in properties
- #Engineering
- #Chemistry
- #Joint Entrance Examination Main
The correct order of the atomic radii of C, Cs, Al and S is :
Option: 1
Option: 2
Option: 3
Option: 4
Periodicity of atomic radius and ionic radius in period -
In a period from left to right the effective nuclear charge increases because the next electron fills in the same shell. So the atomic size decrease.
- wherein
Electronegativity and atomic radius -
The attraction between the outer electrons and the nucleus increases as the atomic radius decreases in a period.
- wherein
Size of atom and ion in a group -
In a group moving from top to the bottom the number of shell increases.So the atomic size increases.
- wherein
As we know that
From Left to right in a period size decreases and when going down the group size increases
Therefore, Option(2) is correct
View Full Answer(1)
Crack CUET with india's "Best Teachers"
- HD Video Lectures
- Unlimited Mock Tests
- Faculty Support

- #Classification of elements and periodicity in properties
- #Engineering
- #Chemistry
- #Joint Entrance Examination Main
The IUPAC symbol for the element with atomic number 119 would be:
Option: 1 uue
Option: 2une
Option: 3 unh
Option: 4 uun
Nomenclature of elements with atomic number >100 -
The name is derived directly from the atomic number of the element using the following numerical roots:
0 = nil
1 = un
2 = bi
3 = tri
4 = quad
5 = pent
6 = hex
7 = sept
8 = oct
9 = enn
Eg:
|
Atomic number |
Name |
Symbol |
|
101 |
Mendelevium (Unnilunium) |
Md (Unu) |
|
102 |
Nobelium (Unnilbium) |
No (Unb) |
-
uue
1 1 9
Un Un ennium
Therefore, Option(1) is correct.
View Full Answer(1)The ammonia released on quantitative reaction of 0.6g, urea
with sodium hydroxide
can be neutralised by:
Option: 1 200 ml of 0.2 N HCl
Option: 2200 ml of 0.4 N HCl
Option: 3100 ml of 0.1N HCl
Option: 4100 ml of 0.2N HCl
2 × mole of Urea = mole of ........(1)
mole of = mole of
........(2)
mole of HCl = 2 × mole of Urea
mole of HCl = ...(i)
[We know , mole = M X V = N X n X V]
...as (i).
Therefore, Option(4) is correct.
View Full Answer(1)JEE Main high-scoring chapters and topics
Study 40% syllabus and score up to 100% marks in JEE
The average molar mass of chlorine is 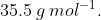 The ratio of
The ratio of 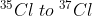 in naturally occurring chlorine is close to :
in naturally occurring chlorine is close to :
Option: 1 4:1
Option: 2 3:1
Option: 3 2:1
Option: 4 1:1
Given,
The average molar mass of chlorine is
Let , the ratio of in naturally occurring chlorine is close to x : y
Now, we know
So,
Therefore, the correct option is (2).
View Full Answer(1)
The minimum number of moles of O2 required for complete combustion of 1 mole of propane and 2 moles of butane is ______
Combustion reaction of 1 mole of propane and 2 moles of butane-

So, Total required mol of O2 = 5 + 13 = 18.
Ans = 18
View Full Answer(1)NEET 2024 Most scoring concepts
- Just Study 32% of the NEET syllabus and Score up to 100% marks
If a person is suffering from the deficiency if nor-adrenaline, what kind of drug can be suggested ?
Option: 1 Anti-inflammatory
Option: 2 Antidepressant
Option: 3 Antihistamine
Option: 4 Analgesic
Non-adrenaline is a neurotransmitter. If nor-adrenaline is low, a person may suffer from depression. Hence, an antidepressant drug is suggested.
Anti-depressant → drug, which enhances the mood.
Therefore, the correct option is (2).
View Full Answer(1)The following molecules act as an :

Option: 1 Antidepranant
Option: 2 Anti-bacterial
Option: 3 Antiseptic
Option: 4 Anti-histamine
Brompheniramine works by blocking the action of histamine, which causes allergic symptoms.
Hence, it acts as an antihistamine.
Therefore, Option(3) is correct.
View Full Answer(1)Crack CUET with india's "Best Teachers"
- HD Video Lectures
- Unlimited Mock Tests
- Faculty Support

The mass of ammonia in grams produced when 2.8 kg of dinitrogen quantitatively reacts with 1 kg of dihydrogen is_________
Option: 1 3400
Option: 2 -
Option: 3 -
Option: 4 -
Given,
2.8 kg of dinitrogen quantitatively reacts with 1 kg of dihydrogen.

From above, the mole of ammonia = 0.2 kMol
So, mass of ammonia = mole X molar mass
mass of ammonia = 0.2 (kMol ) X 17 (g/Mol)
mass of ammonia = 3.4 kg = 3400 g
Ans = 3400
View Full Answer(1)A 100mL solution was made by adding 1.43g of . The normality of the solution is 0.1N. The value of x is___________. (The atomic mass of Na is 23 g/mol)
Molar mass(M) of Na2CO3.xH2O
M = 23 × 2 + 12 + 48 + 18x
M = 46 + 12 + 48 + 18x
M = (106 + 18x)
As nfactor in dissolution will be determined from net cationic or anionic charge; which is 2 so.
Eq.wt. = = (53 + 9x)
As volume = 100 ml = 0.1 Litre
53 + 9x = 143
9x = 90
x = 10.00
Ans = 10
View Full Answer(1)JEE Main high-scoring chapters and topics
Study 40% syllabus and score up to 100% marks in JEE


