-
Engineering and Architecture
Exams
Colleges
Predictors
Resources
-
Computer Application and IT
Quick Links
Colleges
-
Pharmacy
Colleges
Resources
-
Hospitality and Tourism
Colleges
Resources
Diploma Colleges
-
Competition
Other Exams
Resources
-
School
Exams
Top Schools
Products & Resources
-
Study Abroad
Top Countries
Resources
-
Arts, Commerce & Sciences
Colleges
Upcoming Events
Resources
-
Management and Business Administration
Exams
Colleges & Courses
Predictors
-
Learn
Law Preparation
MBA Preparation
Engineering Preparation
Medical Preparation
-
Online Courses and Certifications
Top Streams
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
Resources
-
Medicine and Allied Sciences
Colleges
Predictors
Resources
-
Law
Resources
Colleges
-
Animation and Design
Exams
Predictors & Articles
Colleges
Resources
-
Media, Mass Communication and Journalism
Colleges
Resources
-
Finance & Accounts
Top Courses & Careers
Colleges
Get Answers to all your Questions


- Home
- Engineering
- If are unit vectors such that <img alt="(\vec{a}+\vec{b})
If are unit vectors such that
then angle between
is -
Indeterminate
Answers (1)

As we have learnt in
Scalar, Dot or Inner Product -
Scalar product of two vectors & written as
is a scalar quantity given by the product of the magnitude of
&
and the cosine of the smaller angle between them.
- wherein
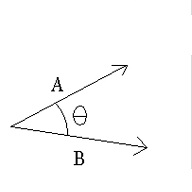
showing the representation of scalar products of vectors.
Vector or cross product -
Vector or cross product of two vectors & written as
is a single vector whose magnitude is equal to the product of the magnitude of
&
and the sine of the smaller angle
between them.
- wherein
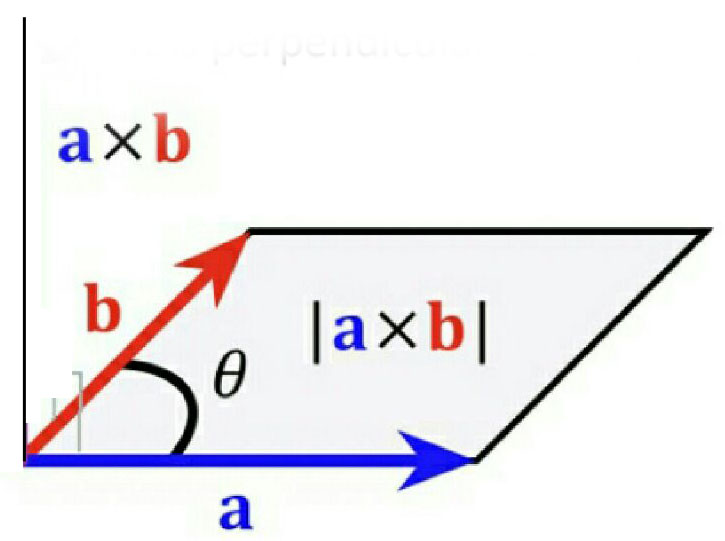
The figure shows the representation of vectors or cross product of vectors.
shows representation of vector or cross product of vectors
which is true for all values of .

