Browse by Stream
-
Engineering and Architecture
Exams
Colleges
Predictors
Resources
-
Computer Application and IT
Quick Links
Colleges
-
Pharmacy
Colleges
Resources
-
Hospitality and Tourism
Colleges
Resources
Diploma Colleges
-
Competition
Other Exams
Resources
-
School
Exams
Top Schools
Products & Resources
-
Study Abroad
Top Countries
Resources
-
Arts, Commerce & Sciences
Exams
Colleges
Upcoming Events
Resources
-
Management and Business Administration
Colleges & Courses
Predictors
-
Learn
Law Preparation
MBA Preparation
Engineering Preparation
Medical Preparation
-
Online Courses and Certifications
Top Streams
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
Resources
-
Medicine and Allied Sciences
Colleges
Predictors
Resources
-
Law
Resources
Colleges
-
Animation and Design
Exams
Predictors & Articles
Colleges
Resources
-
Media, Mass Communication and Journalism
Colleges
Resources
-
Finance & Accounts
Top Courses & Careers
Colleges
Get Answers to all your Questions


- Home
- Engineering
- Let be the solution of the differential equation <img alt="\frac{\mathrm{d} y}{\mathrm{~d} x}=2(y+2 \sin x-5) x-2 \cos x" src="https://entrancecorner.codecogs.com/gif.la
Let 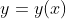 be the solution of the differential equation
be the solution of the differential equation  such that
such that  Then
Then  is equal to:
is equal to:
Option: 1 
Option: 2 
Option: 3 
Option: 4 
Option: 5 
Option: 6 
Option: 7 
Option: 8 
Option: 9 
Option: 10 
Option: 11 
Option: 12 
Option: 13 
Option: 14 
Option: 15 
Option: 16 
Answers (1)

and using by parts in second integral by taking
as second function.
at x = 0, y = 7
Option(3)
View full answer
JEE Main high-scoring chapters and topics
Study 40% syllabus and score up to 100% marks in JEE
Similar Questions
-
5 g of Na2SO4 was dissolved in x g of H2O. The change in freezing point was found to be 3.820C. If Na2SO4 is 81.5% ionised, the value of x (K

A capacitor is made of two square plates each of side 'a' making a very small angle
-
A solution of m-chloroaniline, m-chlorophenol and m-chlorobenzoic acid in ethyl acetate was extracted initially with a saturated solution of NaHCO3 to give fraction A. The leftover organic phase was extracted with d


