Browse by Stream
-
Engineering and Architecture
Exams
Colleges
Predictors
Resources
-
Computer Application and IT
Quick Links
Colleges
-
Pharmacy
Colleges
Resources
-
Hospitality and Tourism
Colleges
Resources
Diploma Colleges
-
Competition
Other Exams
Resources
-
School
Exams
Top Schools
Products & Resources
-
Study Abroad
Top Countries
Resources
-
Arts, Commerce & Sciences
Exams
Colleges
Upcoming Events
Resources
-
Management and Business Administration
Colleges & Courses
Predictors
-
Learn
Law Preparation
MBA Preparation
Engineering Preparation
Medical Preparation
-
Online Courses and Certifications
Top Streams
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
Resources
-
Medicine and Allied Sciences
Colleges
Predictors
Resources
-
Law
Resources
Colleges
-
Animation and Design
Exams
Predictors & Articles
Colleges
Resources
-
Media, Mass Communication and Journalism
Colleges
Resources
-
Finance & Accounts
Top Courses & Careers
Colleges
Get Answers to all your Questions


- Home
- Engineering
- The shortest wavelength of H atom in the Lyman series is . The longest wavelength in the Balmer series He+ is:Option: 1 <img alt="\
The shortest wavelength of H atom in the Lyman series is 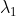 . The longest wavelength in the Balmer series He+ is:
. The longest wavelength in the Balmer series He+ is:
Option: 1 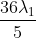
Option: 2 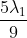
Option: 3 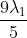
Option: 4 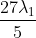
Answers (1)

We know,
So, for
minimum(Shortest)
for f H atoms in the Lyman series n = 1 & for Transition must be form n =
to n = 1,
Z = 1
For longest wavelength for Balmer series n = 3 to n = 2 will have
for He+ , Z = 2
Therefore, the correct option is (3).
View full answer
JEE Main high-scoring chapters and topics
Study 40% syllabus and score up to 100% marks in JEE


