-
Engineering and Architecture
Exams
Colleges
Predictors
Resources
-
Computer Application and IT
Quick Links
Colleges
-
Pharmacy
Colleges
Resources
-
Hospitality and Tourism
Colleges
Resources
Diploma Colleges
-
Competition
Other Exams
Resources
-
School
Exams
Top Schools
Products & Resources
-
Study Abroad
Top Countries
Resources
-
Arts, Commerce & Sciences
Colleges
Upcoming Events
Resources
-
Management and Business Administration
Exams
Colleges & Courses
Predictors
-
Learn
Law Preparation
MBA Preparation
Engineering Preparation
Medical Preparation
-
Online Courses and Certifications
Top Streams
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
Resources
-
Medicine and Allied Sciences
Colleges
Predictors
Resources
-
Law
Resources
Colleges
-
Animation and Design
Exams
Predictors & Articles
Colleges
Resources
-
Media, Mass Communication and Journalism
Colleges
Resources
-
Finance & Accounts
Top Courses & Careers
Colleges
Get Answers to all your Questions


All Questions
5 g of Na2SO4 was dissolved in x g of H2O. The change in freezing point was found to be 3.820C. If Na2SO4 is 81.5% ionised, the value of x (K for water=1.860C kg mol−1) is approximately : (molar mass of S=32 g mol−1 and that of Na=23 g mol−1)
Option: 1 15 g
Option: 2 25 g
Option: 3 45 g
Option: 4 65 g
View Full Answer(1)
The freezing point of benzene decreases by 0.450C when 0.2 g of acetic acid is added to 20 g of benzene. If acetic acid associates to form a dimer in benzene, percentage association of acetic acid in benzene will be : (Kf for benzene=5.12 K kg mol−1)
Option: 1 74.6%
Option: 2 94.6
Option: 3 64.6%
Option: 4 80.4%
In benzene ,
t = 0 1 -
t = t 1 -
Given:
w = 0.2g W = 20 g T = 0.45 K
As we know ,
, observed M = 113.78 (acetic acid)
Molecular weight of acetic acid = 60
% degree of association = 94.5 %
View Full Answer(1)Crack CUET with india's "Best Teachers"
- HD Video Lectures
- Unlimited Mock Tests
- Faculty Support

At room temperature, a dilute solution of urea is prepared by dissolving 0.60g of urea in 360 g of water. If the vapour pressure of pure water at this temperature is 35 mmHg, lowering of vapour pressure(in mmHg) will be: (molar mass of urea = 60g/mol)
Option: 1 0.017
Option: 2 0.028
Option: 3 0.027
Option: 4 0.031
Molecular weight of urea = 60 g / mol
Now, we know that :
Relative lowering of vapour pressure is equal to the molar mass of the solute.
option (1) is correct.
View Full Answer(1)
The elevation of boiling point of 0.1 m aq solution is two times that of 0.05 aq.
solution. The value of x _____ (Assume 100% ionization of complex and
, coordination number of Cr is 6 and that all of
molecules are present inside the coordination sphere.)
Thus, i = 3
Therefore, the complex is dissociated into 3 ions.
Hence, complex is
Thus, the value is 5.
View Full Answer(1)JEE Main high-scoring chapters and topics
Study 40% syllabus and score up to 100% marks in JEE
A set of solutions is prepared using 180 g of water as a solvent and 10 g of different non-volatile solutes A,B and C. The relative lowring of vapour pressure in the presence of these solutes are in the order [Given, molar mass of A=100 g mol -1; B=200 g mol -1; C=10,000 g mol -1]
Option: 1 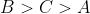
Option: 2 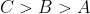
Option: 3 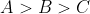
Option: 4 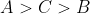
Here vapour pressure of water is lowering.
We know this formula,
Partial Vapour pressure of water Pwater = PoXwater
Lowering Vapour pressure of water = Po – Pwater
The relative lowering of vapour pressure
Now,
From above,
How much amount of NaCl (in grams) should be added to 600g of water to decrease the freezing point of water to ? (Assume that the freezing point depression constant for water = 2K kg mol-1)
Option: 1 1.76
Option: 2 3.52
Option: 3 4.9
Option: 4 8.58
NEET 2024 Most scoring concepts
- Just Study 32% of the NEET syllabus and Score up to 100% marks
The osmotic pressure of a solution of NaCl is 0.10 atm and that of a glucose solution is 0.20 atm. The osmotic pressure of a solution formed by mixing 1L of the sodium chloride solution 2L of the glucose solution is . x is _________ (nearest interger)
We know this formula.
Ans = 167
------------------------------------------
Alternate Solution

Ans = 167
View Full Answer(1)The mole fraction of glucose in an aqueous binary solution is 0.1. The mass percentage of water in it to the nearest integer is-
Mole fraction of glucose, in
Now, lets assume we have 10 moles of solution.
Thus, moles of
Ans, moles of
Now, the mass of water = number of moles x molar mass
Thus, the mass of water
Mass of
Now, mass percent of water is given as:
Thus, the correct answer is 47.
View Full Answer(1)Crack CUET with india's "Best Teachers"
- HD Video Lectures
- Unlimited Mock Tests
- Faculty Support

If of an aqueous solution containing
of a protein A is isotonic with one litre of another aqueous solution containing
of a protein
, AT
, the ratio of the molecular masses of
and
is ______
(to the nearest integer).
Let molar mass of protein A = x g/mol
Let molar mass of protein B = y g/mol
Now,
Ans = 177
View Full Answer(1)2 molal solution of a weak acid HA has a freezing point of 3.885oC. The degree of dissociation of this acid is _________ (Round off to the Nearest Integer). [Given : Molal depression constant of water
Freezing point of pure water = 0o C]
Given,
2 molal solution of a weak acid HA has a freezing point of 3.885ºC.
m = 2
Molal depression constant of water (Kf) = 1.85 K kg mol-1
The freezing point of pure water Ti = 0ºC
van't Hoff factor i is related to the degree of dissociation \alpha as, if n = number of ions,
Here n = 2 (H+and A-)
So,
We know the formula of depression at the freezing point.
i = 1.05
Now,
Ans = 50
View Full Answer(1)JEE Main high-scoring chapters and topics
Study 40% syllabus and score up to 100% marks in JEE


