-
Engineering and Architecture
Exams
Colleges
Predictors
Resources
-
Computer Application and IT
Quick Links
Colleges
-
Pharmacy
Colleges
Resources
-
Hospitality and Tourism
Colleges
Resources
Diploma Colleges
-
Competition
Other Exams
Resources
-
School
Exams
Top Schools
Products & Resources
-
Study Abroad
Top Countries
Resources
-
Arts, Commerce & Sciences
Colleges
Upcoming Events
Resources
-
Management and Business Administration
Exams
Colleges & Courses
Predictors
-
Learn
Law Preparation
MBA Preparation
Engineering Preparation
Medical Preparation
-
Online Courses and Certifications
Top Streams
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
Resources
-
Medicine and Allied Sciences
Colleges
Predictors
Resources
-
Law
Resources
Colleges
-
Animation and Design
Exams
Predictors & Articles
Colleges
Resources
-
Media, Mass Communication and Journalism
Colleges
Resources
-
Finance & Accounts
Top Courses & Careers
Colleges
Get Answers to all your Questions


All Questions
An ideal gas undergoes a quasi static, reversible process in which its molar heat capacity C remains constant. If during this process the relation of pressure P and volume V is given by PVn=constant, then n is given by (Here CP and CV are molar specific heat at constant pressure and constant volume, respectively)
Option: 1
Option: 2
Option: 3
Option: 4
For a polytropic preocess
The temperature of an open room of volume 30 m3 increases from 170C to 270C due to the sunshine. The atmospheric pressure in the room remains 1×105 Pa. If and
are the number of molecules in the room before and after heating, then
will be :
Option: 1 −1.61×1023
Option: 2 1.38×1023
Option: 3 2.5×1025
Option: 4 −2.5×1025
PV = nRT
change in Number of molecules
Correct option is 4.
View Full Answer(1)Crack CUET with india's "Best Teachers"
- HD Video Lectures
- Unlimited Mock Tests
- Faculty Support

The plot that depicts the behavior of the mean free time (time between two successive collisions) for the molecules of an ideal gas, as a function of temperature (T), qualitatively, is: (Graphs are schematic and not drawn to scale)
Option: 1 
Option: 2 
Option: 3 
Option: 4 
As relaxation time is given as
where λ=mean free path
and
while
where N=number of molecules per unit volume
So keeping all the other quantities are constant.
we get
So the correct graph is given in option 2
View Full Answer(1)Two moles of an ideal gas with are mixed 3 moles of another ideal gas with
. The value of
for the mixture is:-
Option: 1
Option: 2
Option: 3
Option: 4
For ideal gas:-
For first case:-
So,
For second case:-
and
Now,
So option (4) is correct.
View Full Answer(1)JEE Main high-scoring chapters and topics
Study 40% syllabus and score up to 100% marks in JEE
Two gases-argon (atomic radius 0.07 nm, atomic weight 40) and xenon ( atomic radius 0.1 nm, atomic weight 140) have the same number density and are at the same temperature. The ratio of their respective mean free times is closest to :
Option: 1
Option: 2
Option: 3
Option: 4 1.07
Mean free time
View Full Answer(1)
Consider a mixture of n moles of helium gas and 2n moles of oxygen gas (molecules taken to be rigid) as an ideal gas. Its Cp/Cv value will be :
Option: 1 40/27
Option: 2 23/15
Option: 3 19/13
Option: 4 67/45
For monoatomic gas (He)
For diatomic gas (O2)
Hence the correct option is (3).
View Full Answer(1)NEET 2024 Most scoring concepts
- Just Study 32% of the NEET syllabus and Score up to 100% marks
Under an adiabatic process, the volume of an ideal gas gets doubled. Consequently the mean collision time between the gas molecule changes from to
. If
for this gas then a good estimate for
is
Option: 1
Option: 2
Option: 3
Option: 4
As, relaxation time=
and using gives
Consider two ideal diatomic gases A and B at same temperature T. Molecules of the gas A are rigid and have a mass m. Molecules of the gas B have an additional vibrational mode and have a mass . The ratio of the specific heats
of gas A and B respectively is:
Option: 1 5:9
Option: 2 7:9
Option: 3 3:5
Option: 4 5:7
Molar heat capacity of A at constant volume
Molar heat capacity of B at constant volume
Dividing both
Hence the correct option is (4).
View Full Answer(1)Crack CUET with india's "Best Teachers"
- HD Video Lectures
- Unlimited Mock Tests
- Faculty Support

The RMS speeds of the molecules of Hydrogen , Oxygen and Carbon dioxide at the same temperature are 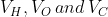 respectively then:
respectively then:
Option: 1 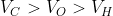
Option: 2 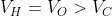
Option: 3 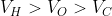
Option: 4 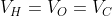
The correct option is (3)
The temperature of equal masses of three ifferent liquids x,y and z are 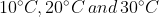 respectively.The temperature of mixture when x is mixed with y is
respectively.The temperature of mixture when x is mixed with y is 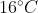 and that when y is mixed with z is
and that when y is mixed with z is 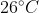 , The temperature of mixture when x and z are mixed will be :
, The temperature of mixture when x and z are mixed will be :
Option: 1 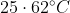
Option: 2 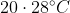
Option: 3 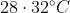
Option: 4 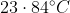
For x & y mixture ,
Mixture of y & Z
Mixture of x & z
From eqn (1)
The correct option is (4)
JEE Main high-scoring chapters and topics
Study 40% syllabus and score up to 100% marks in JEE


