Browse by Stream
-
Engineering and Architecture
Exams
Colleges
Predictors
Resources
-
Computer Application and IT
Quick Links
Colleges
-
Pharmacy
Colleges
Resources
-
Hospitality and Tourism
Colleges
Resources
Diploma Colleges
-
Competition
Other Exams
Resources
-
School
Exams
Top Schools
Products & Resources
-
Study Abroad
Top Countries
Resources
-
Arts, Commerce & Sciences
Colleges
Upcoming Events
Resources
-
Management and Business Administration
Exams
Colleges & Courses
Predictors
-
Learn
Law Preparation
MBA Preparation
Engineering Preparation
Medical Preparation
-
Online Courses and Certifications
Top Streams
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
Resources
-
Medicine and Allied Sciences
Colleges
Predictors
Resources
-
Law
Resources
Colleges
-
Animation and Design
Exams
Predictors & Articles
Colleges
Resources
-
Media, Mass Communication and Journalism
Colleges
Resources
-
Finance & Accounts
Top Courses & Careers
Colleges
Get Answers to all your Questions


- #1.3
- #8.6
- #Fill in the blanks
- #Short Answer type
- #Long answer type
- #True-false based type
- #Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
- 1.0
- 2.0
- 3.0
- 4.0
- 5.0
- 6.0
- 7.0
- 8.0
- 9.0
- 10.0
- 11.0
- 12.0
- 13.0
- 14.0
- 15.0
- 16.0
- 17.0
- 18.0
- 19.0
- 20.0
- 21.0
- 22.0
- 23.0
- 24.0
- 25.0
- 26.0
- 27.0
- 28.0
- 29.0
- 30.0
- 31.0
- 32.0
- 33.0
- 34.0
- 35.0
- 36.0
- 37.0
- 38.0
- 39.0
- 40.0
- 41.0
- 42.0
- 43.0
- 44.0
- 45.0
- 46.0
- 47.0
- 48.0
- 49.0
- 50.0
- 51.0
- 52.0
- 53.0
- 54.0
- 55.0
- 56.0
- 57.0
- 58.0
- 59.0
- 60.0
- 61.0
- 62.0
- 67.0
- 68.0
- 69.0
- 70.0
- 71.0
- 72.0
- 73.0
- 74.0
- 75.0
- 76.0
- 77.0
- 79.0
- 81.0
- 83.0
- 85.0
- 86.0
- 87.0
- 88.0
- 89.0
- 90.0
- 91.0
- 92.0
- 93.0
- 94.0
- 95.0
- 96.0
- 97.0
- 98.0
- 99.0
- 100.0
- 101.0
- 102.0
- 104.0
- 105.0
Let 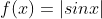 . Then
. Then
A. f is everywhere differentiable
B. f is everywhere continuous but not differentiable 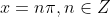
C. f is everywhere continuous but not differentiable at 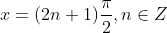
D. None of these
A. f is everywhere differentiable
B. f is everywhere continuous but not differentiable
C. f is everywhere continuous but not differentiable at
D. None of these
Answers (1)
B)
Given that,
Let g(x) = sinx and h(x) = |x|
Then, f(x) = hog(x)
We know that, modulus function and sine function are continuous everywhere.
Since, composition of two continuous functions is a continuous function.
Hence, f(x) = hog(x) is continuous everywhere.
Now, v(x)=|x| is not differentiable at x=0.
So, f(x) is not differentiable where
We know that at
Hence, f(x) is everywhere continuous but not differentiable
View full answer
Similar Questions
- 100 g of liquid A (molar mass 140 g mol^-1) was dissolved in 1000 g of liquid B (molar mass 180 g mol^-1).The vapour pressure of pure liquid B was found to be 500 torr.
- 100 turn rectangular coil ABCD (in X-Y plane) is hung from one arm of a balance (shown in figure). A mass 500 g is added to the other arm to balance the weight of the coil.
- 100m long antenna is mounted on a 500m tall building The complex can become a transmission tower for waves with λ (a) ~ 400 m (b) ~ 25 m (c) ~ 150 m (d) ~ 2400 m

