-
Engineering and Architecture
Exams
Colleges
Predictors
Resources
-
Computer Application and IT
Quick Links
Colleges
-
Pharmacy
Colleges
Resources
-
Hospitality and Tourism
Colleges
Resources
Diploma Colleges
-
Competition
Other Exams
Resources
-
School
Exams
Top Schools
Products & Resources
-
Study Abroad
Top Countries
Resources
-
Arts, Commerce & Sciences
Colleges
Upcoming Events
Resources
-
Management and Business Administration
Exams
Colleges & Courses
Predictors
-
Learn
Law Preparation
MBA Preparation
Engineering Preparation
Medical Preparation
-
Online Courses and Certifications
Top Streams
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
Resources
-
Medicine and Allied Sciences
Colleges
Predictors
Resources
-
Law
Resources
Colleges
-
Animation and Design
Exams
Predictors & Articles
Colleges
Resources
-
Media, Mass Communication and Journalism
Colleges
Resources
-
Finance & Accounts
Top Courses & Careers
Colleges
Get Answers to all your Questions


All Questions
Element forms ccp structure and
occupies half of the octahedral voids, while oxygen atoms occupy all the tetrahedral voids. The structure of bimetallic oxide is :
Option: 1
Option: 2
Option: 3
Option: 4
Voids -
Voids are empty spaces in a unit cell. They are of four types: triangular, tetrahedral, octahedral, cubic.
-
B forms ccp structure (FCC)
Number of atoms per unit cell of
occupies half of the octahedral voids.
Number of atoms of element
atoms occupy all the tetrahedral voids.
Number of atoms of
[2 Td voids on 4 Body diagonal]
Structure of bimetallic oxide is :-
Mischmetal is an alloy consisting mainly of :
Option: 1 lanthanoid metals
Option: 2 actionoid and transition metals
Option: 3 Lanthanoid and actionoid metals
Option: 4 actionoid metals
Mischmetal is an alloy of lanthanoid metals with Fe.
It consists of a lanthanoid metal (~95%) and iron (~5%) and traces of S, C, Ca, and Al.
Therefore, the correct option is (1).
View Full Answer(1)Crack CUET with india's "Best Teachers"
- HD Video Lectures
- Unlimited Mock Tests
- Faculty Support

The incorrect statement(s) among (a)-(c) is (are):
(a) W(VI) is more stable than Cr(VI)
(b) in the presence of HCl, permaganate titrations provide satisfactory results.
(c) some lanthnoid oxides can be used as phosphorous
Option: 1 (b) and (c) only
Option: 2 (a) and (b) only
Option: 3 (b) only
Option: 4 (a) only
(a) W(VI) is more stable than Cr(VI). It is true and given in NCERT.
(b) in the presence of HCl permanganate titrations provide satisfactory results. It is incorrect.
Permanganate titrations in presence of hydrochloric acid are unsatisfactory since hydrochloric acid is oxidised to chlorine.
(c) Some individual Ln oxides are used as phosphors in television screens and similar fluorescing surfaces.
So,(b) is incorrect.
Therefore, the correct option is (3).
View Full Answer(1)- #The P Block Elements (Group 13 and Group 14)
- #Engineering
- #Chemistry
- #Joint Entrance Examination Main
The reaction white phosphorus on boiling with alkali in inert atmosphere resulted inthe formation of product 'A'. The reaction of 1 mol of 'A' with excess of 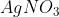 in aqueous medium gives ________mol (s) of
in aqueous medium gives ________mol (s) of 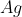 . (Round off to the Nearest Integer).
. (Round off to the Nearest Integer).
Option: 1 4
Option: 2 -
Option: 3 -
Option: 4 -
The reaction of white phosphorus on boiling with alkali in the inert atmosphere resulted in the formation of the product 'A'.
The reaction 1 mol of 'A' with an excess of AgNO3 in an aqueous medium gives 4 moles of Ag.
Ans = 4
View Full Answer(1)JEE Main high-scoring chapters and topics
Study 40% syllabus and score up to 100% marks in JEE
One of the by-products formed during the recovery of NH3 from Solvay process is :
Option: 1 NaHCO3
Option: 2 CaCl2
Option: 3 Ca(OH)2
Option: 4 NH4Cl
On a small scale ammonia is obtained from ammonium salts which decompose when treated with caustic soda or calcium hydroxide.
Recovery of NH3

Therefore, the Correct option is (2)
View Full Answer(1)The set of elements that differ in mutual relationship from those of the other sets is :
Option: 1 B – Si
Option: 2 Li – Mg
Option: 3 Be – Al
Option: 4 Li – Na
Mutual relationships can be anything.
Li–Mg, B–Si, Be–Al show diagonal relationship but Li and Na do not show diagonal relationship as both belongs to the same group and not placed diagonally.
Therefore, the Correct option is (4)
View Full Answer(1)NEET 2024 Most scoring concepts
- Just Study 32% of the NEET syllabus and Score up to 100% marks
Given below are two statements : Statement I : The value for
is
Statement II :
is more stable in
state than
state. In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below :
Option: 1 Both statement I and statement II are correct
Option: 2 Both statement I and statement II are incorrect
Option: 3 Statement I is incorrect but statement II is correct
Option: 4 Statement I is correct but statement II is incorrect
The Eo value for Ce4+/Ce3+ is +1.74 V because the most stable oxidation state of lanthanide series elements is +3.
It means Ce3+ is more stable than Ce4+
View Full Answer(1)A group 15 element, which is a metal and forms a hydride with strongest reducing power among group 15 hydrides. The element is :
Option: 1 Bi
Option: 2 As
Option: 3 Sb
Option: 4 P
N, P are Non-Metal
As, Sb are Metalloid
Bi is Metal
Hydrides of group 15 elements are
NH3 , PH3 , AsH3 , SbH3 , BiH3
In NH3, the hydrogen atom gets a partial positive charge due to less electronegativity. But in BiH3, the hydrogen atom gets a partial negative charge because hydrogen is more electronegative than bismuth.
BiH3 is a strong reducing agent than others because we know that H- is a strong reducing agent and Bi – H bond dissociation energy is very less.
View Full Answer(1)Crack CUET with india's "Best Teachers"
- HD Video Lectures
- Unlimited Mock Tests
- Faculty Support

Given below are two statements : Statement I : Both CaCl2.6H2O and MgCl2.8H2O undergo dehydrationon heating. Statement II : BeO is amphoteric whereas the oxides of other elements in the same group are acidic. In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Option: 1 Statement I is false but statement II is true
Option: 2 Both statement I and Statement II are false
Option: 3 Statement I is true but statement II is false
Option: 4 Both statement I and Statement II are true
The dehydration of hydrated chloride of calcium can be achieved. The corresponding hydrated chloride of magnesium on heating suffer hydrolysis.
MgO, CaO, SrO, BaO All are basic oxides.
So, Both Statement I and Statement II are false
View Full Answer(1)Assertaion and Reasoning question: (i) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are correct statements, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A). (ii) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are correct statements, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A). (iii) Assertion (A) is correct, but Reason (R) is incorrect statement. (iv) Assertion (A) is incorrect, but Reason (R) is correct statement. Assertion (A) : F – F bond in F2 molecule is weak. Reason (R) : F atom is small in size
(ii) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are correct statements, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
View Full Answer(1)JEE Main high-scoring chapters and topics
Study 40% syllabus and score up to 100% marks in JEE


